In Part 1 and Part 2 of this series, we looked at some of the intriguing aspects of the way people’s everyday lives are affected by design in Japan. Whether the result of a lone designer with a singular focus or a meddling committee with a medley of requirements, it’s fascinating to see how other countries have approached the same challenges.
A big part of this includes the built landscape, and today I wanted to look at Tokyo’s ever-changing skyline which has been the result of natural disasters, war, and cultural beliefs.
Disposable Houses
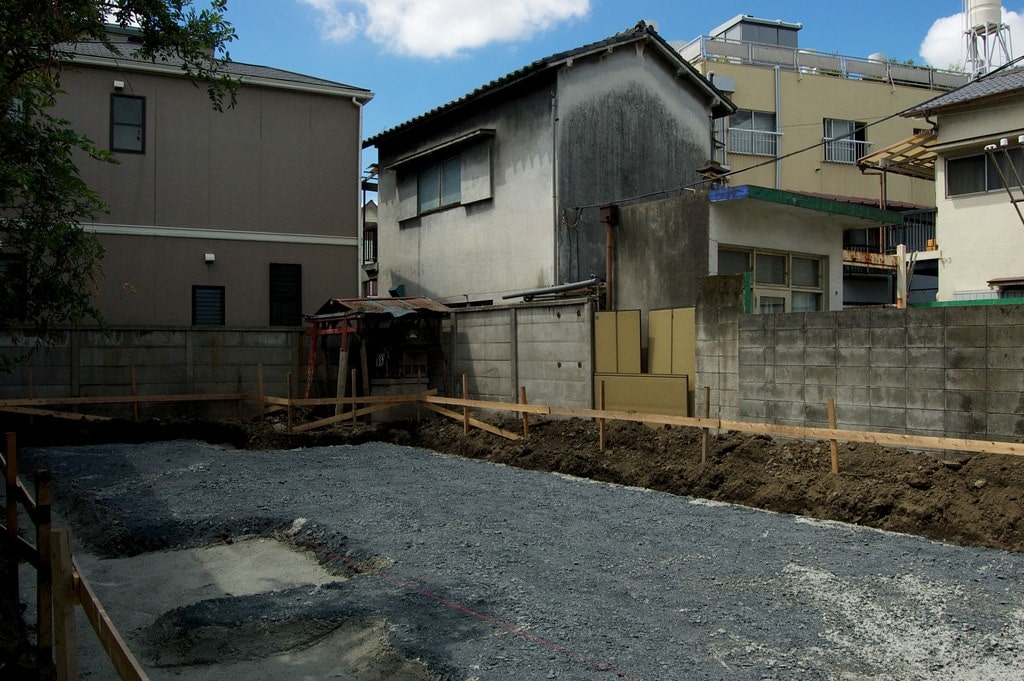

- The resale market in Japan for used houses is almost non-existent (likewise for cars)
- Housing quality is very high but a detached house fully loses its value after 15-30 years
- 50% of houses are demolished before they are 38 years old (compared to 100 in the U.S.)
- Earthquakes cause people to view houses as perishable and builders play on this fear
- Japanese society values newness as something which is spiritually clean and pure
- There are more registered architects per capita in Japan than in any other country
- Huge demand for creatively designed homes but no economic incentive to maintain
More insight into this phenomenon on a recent Freakonomics Radio podcast episode.
Sliced Buildings
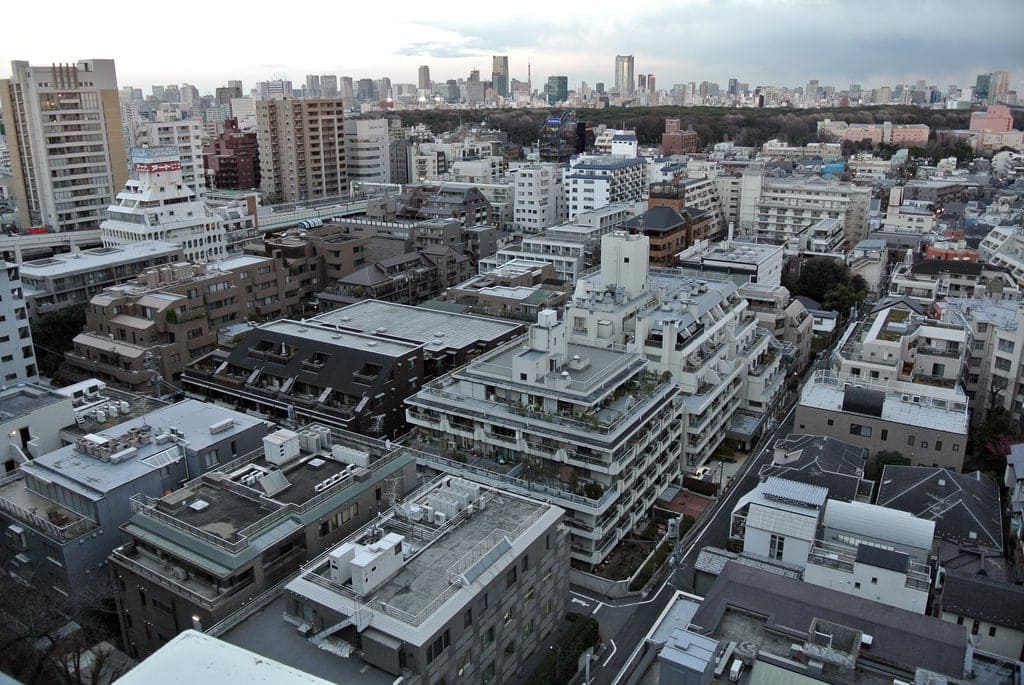

- In Japan, many mid-height buildings look like they’ve had their sides sliced off by design
- Building regulations stipulate a sloping plane that originates from the plot boundary
- Intended to ensure that natural light can still reach the street and neighbouring properties
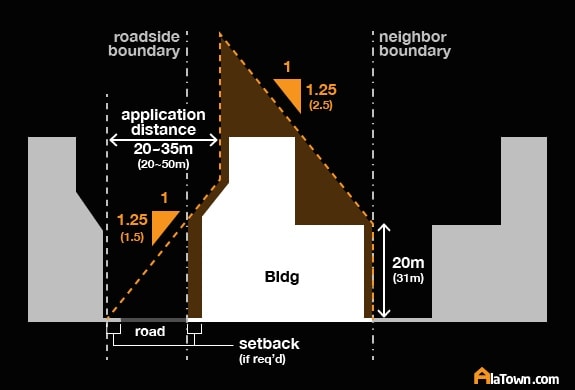
The law results in some very interesting shaped buildings when multiple slanted planes bisect.
Inverse Addresses
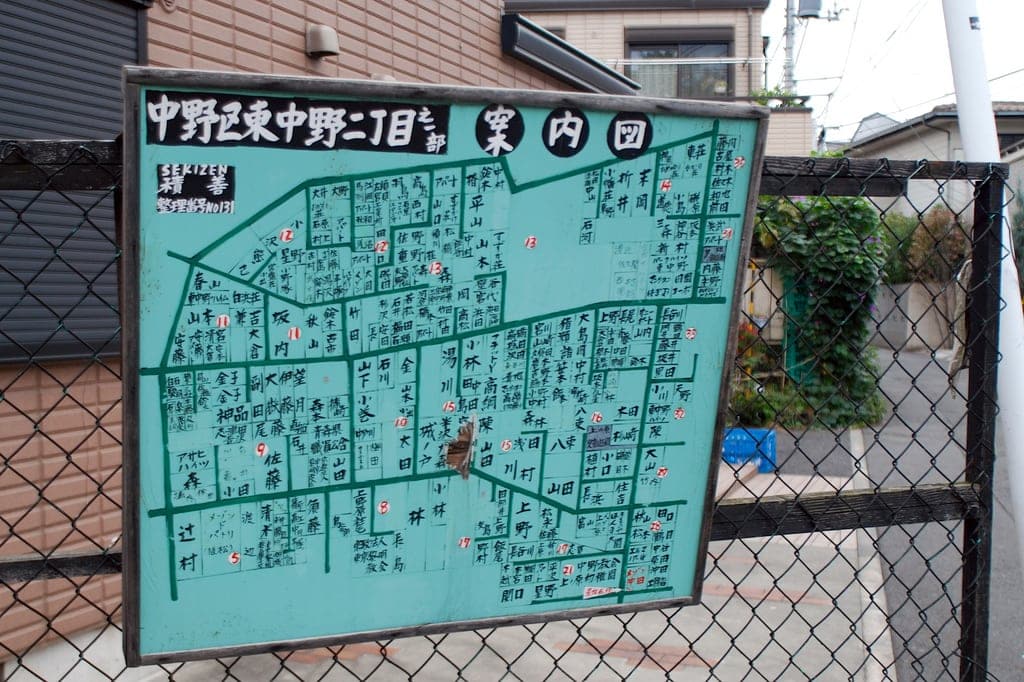
- Most streets in Japan don’t have names, however, the blocks between streets are numbered
- Buildings within a block are also numbered in the order in which they were historically built
- Addresses are written starting from the biggest to smallest geographic entities
If that doesn’t make much sense this video by Derek Sivers should clear things up.
Vending Machines (自動販売機)
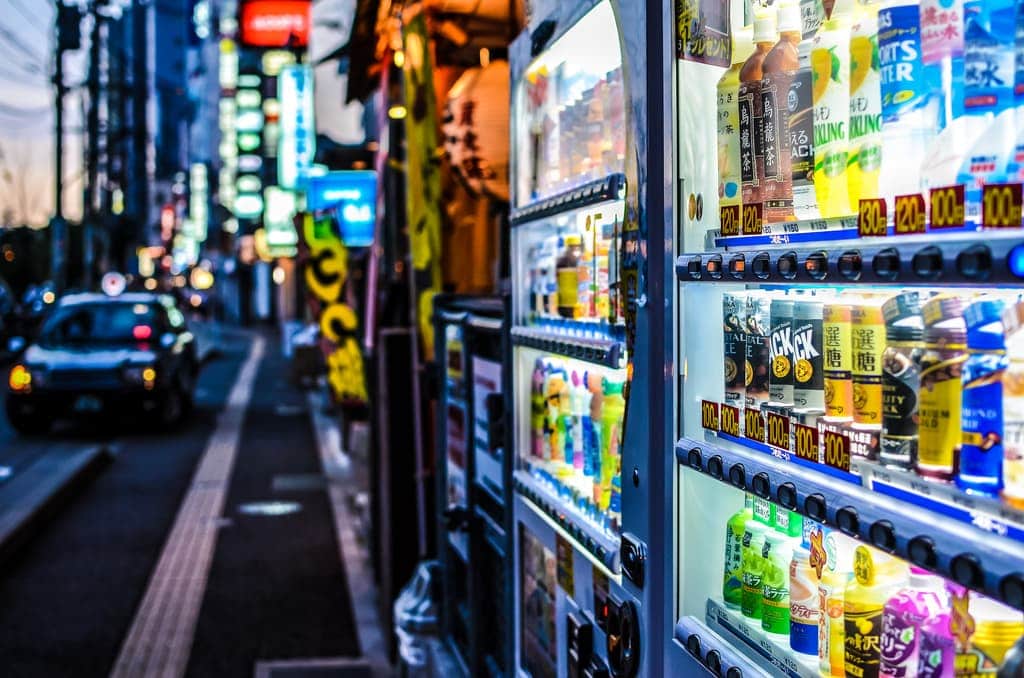

- There is around 1 vending machine for every 23 people in Japan selling all manner of things
- Can be found on almost every street corner and modern ones have huge touchscreen displays
- Cigarettes and alcohol required an age-restricted IC card but it’s easily circumvented
- Some are equipped with a feature that provides free drinks after a major earthquake
Queuing Culture

- Without exaggeration, the Japanese are masters of queuing no matter how mundane
- Whether a restaurant, train, theme park, shop, football match or shrine it’s always orderly
- Queuing for hours becomes part of the experience of enjoying something popular or new
Surgical Masks
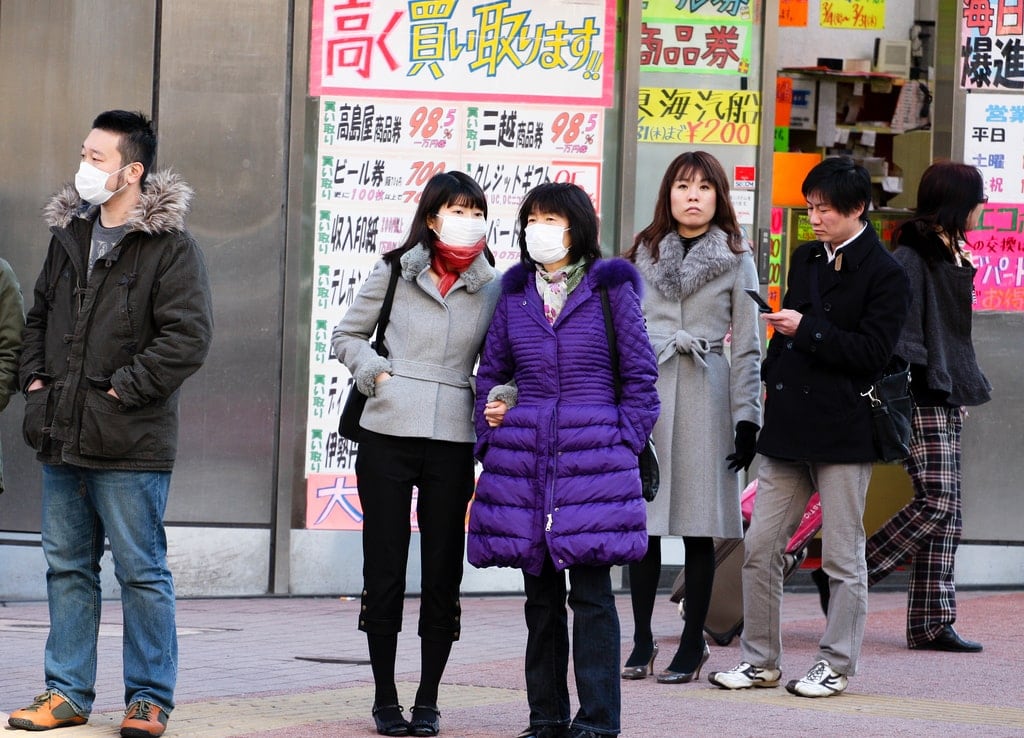

- Worn by those with colds to prevent the spread of infections and show social responsibility
- Have antimicrobial coatings which release toxic O3, killing germs such as MSRA
- Some wear masks in an attempt to minimise the effects of pollen allergies (花粉症)


Reply